What if you put fish to work to fertilize plants? Aquaponics does just that. It creates a symbiotic environment between fish or other aquatic creatures and the plants they fertilize.
Using simple principles and innovative designs, aquaponics can be used in the home as well as on a large scale. It can help you garden indoors and enjoy faster crops and better use of resources compared to traditional methods.
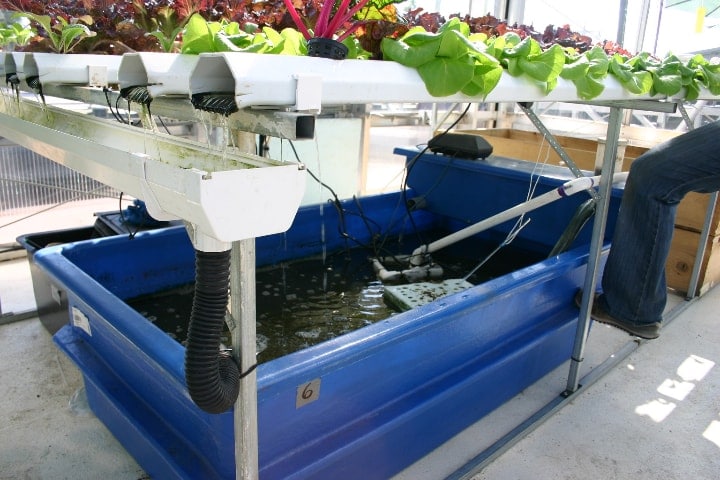

In this post, you’ll find out more about aquaponics pros and cons, the different aquaponic systems out there, and how to get started. But first, let’s define aquaponics more clearly.
Aquaponics Definition
Aquaponics combines aquaculture with hydroponics to create a self-sustainable environment where both plants and animals can thrive.
Conventional aquaculture, or the raising of aquatic animals in tanks, leads to the accumulation of animal excretions. This type of waste increases the toxicity of the water.
That’s where hydroponics comes in. Hydroponics is the ancient practice of cultivating plants in water as a growing medium.
It does away with soil to speed up growth and increase yields. We wrote a full guide on hydroponics if you’re interested in learning more about the different hydroponic systems.
Aquaponics circulate the water in an aquaculture system through a hydroponic system to break down by-products into nutrients and return clean water to the fish.
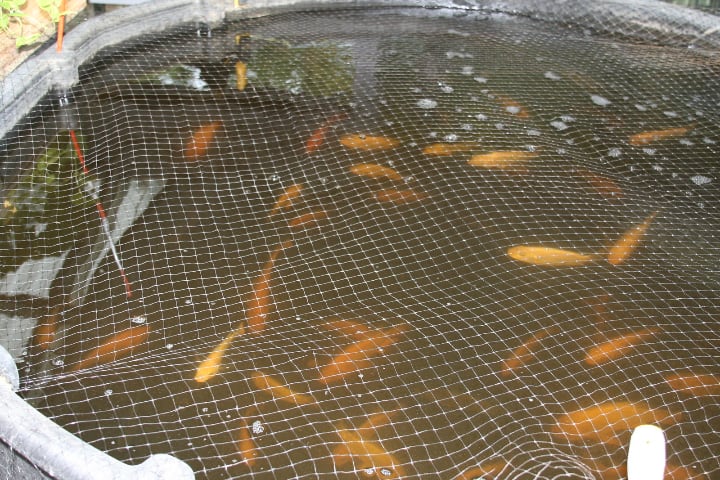

Fact: Aquaponics relies on nitrifying bacteria to turn waste into nitrites and then into nitrates that feed the plants.
Put another way, aquaponics is a way of putting fish to work by feeding them and then using their waste as a natural fertilizer for plants.
When balanced, the amount of waste produced by fish is offset by the plant’s ability to use it. Here’s a simple overview of this system in action:
- Ammonia is added to water via the waste of the fish
- Water with ammonia is pomped to the plant-bacteria tanks
- The bacteria convert the ammonia into Nitrate
- The plant food (Nitrate) is absorbed by the plants
- Clean water is returned to the fish tank
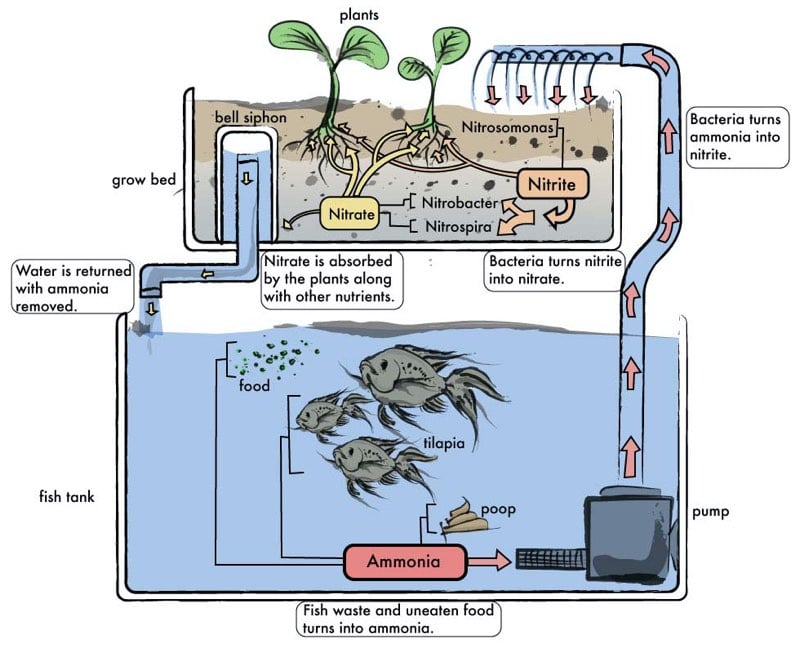
Inspired by natural processes, aquaponics uses aquatic life, bacteria, and nutrient dynamics to recreate the conditions found in waterways.
By doing so, it brings together the key benefits of both aquaculture and hydroponics while minimizing the drawbacks of each. Pretty cool, right?
Advantages of Aquaponic Farming
Aquaponic farming comes with several notable benefits. If you’re thinking about getting started with it, these benefits can be inspiring. Read on to discover them.
Efficient Water Use
All aquaponic systems use less water than a conventional farm would. That’s because aquaponics recirculates water instead of letting it evaporate.
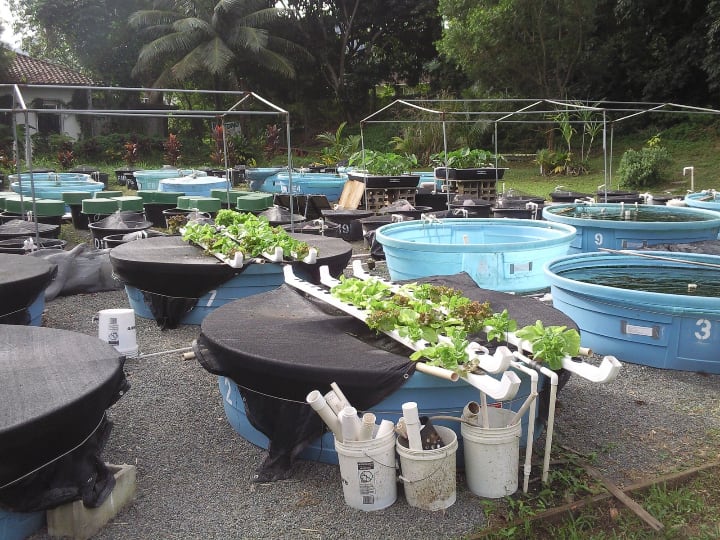

That’s more environmentally friendly than standard farming methods. And that’s important when you consider that agriculture accounts for 70% of global water withdrawals and encourages water scarcity.
Self-Sustainable
Once you set up an aquaponic system, it can pretty much run on its own. Some systems do require more cleaning than others.
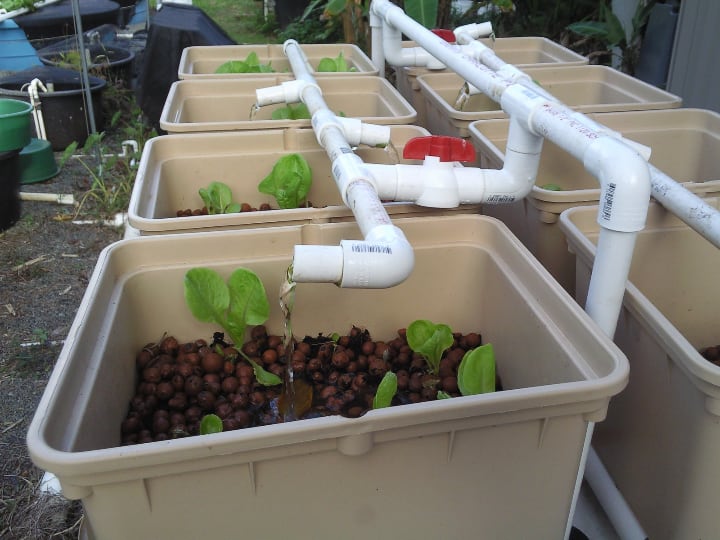

But other than that, you don’t have to keep an eye on it all the time. In other words, aquaponics can be not just effective but also liberating.
Reduced Human Labor
With aquaponic farming, you put the fish to work. You don’t have to worry about manually working the soil or fertilizing the plants. You can reduce human labor significantly.
Environmental Benefits
Aquaponics reproduces ecological cycles found in nature. Not only does it save land, but it does away with pesticides and fertilizers. The best part?
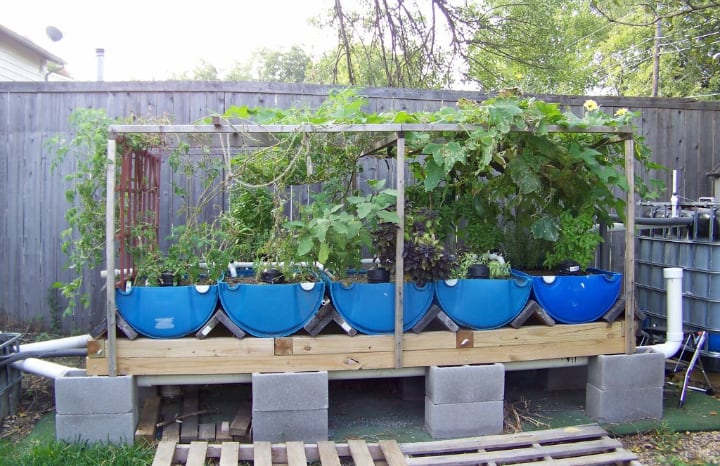

Buildings such as warehouses can be converted into aquaponic facilities in pretty much in any location.
Disadvantages of Aquaponic Farming
It’s only fair to note that aquaponics has a couple of drawbacks too. Knowing about them can help you anticipate potential problems. Also, it can help you invest in the right aquaponic system.
Requires Plenty of Electricity
An aquaponic system requires a pump and possibly a light source and heating. In an indoor setting, all these have to run continuously.
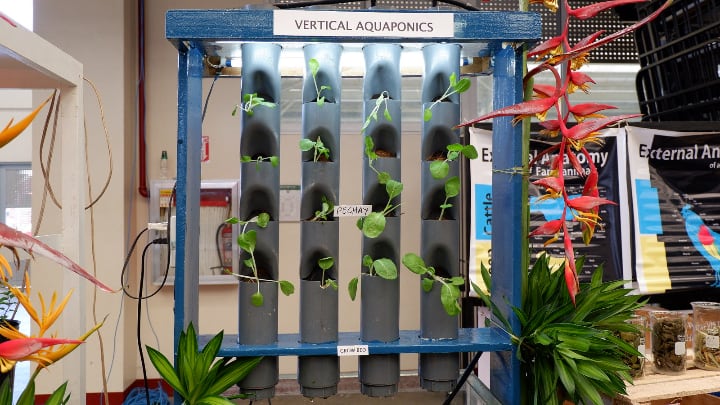

As you may imagine, this can add up to the costs associated with the initial investment, and especially during the winter.
However, installing solar panels and other renewable energy systems can reduce energy consumption.
Initial Investment
An aquaponic system tends to cost more than a hydroponic system because of the aquaculture equipment it requires.
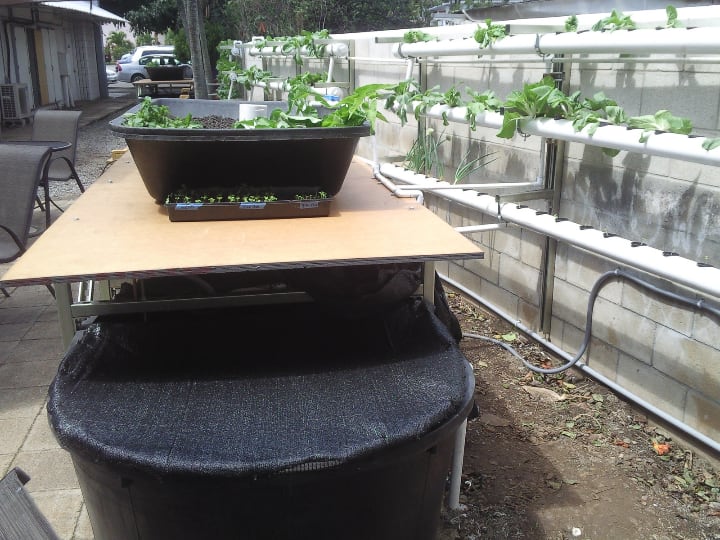

Also, you have to buy the fish and food for them. These costs can add up, especially when you use aquaponics in a commercial setting.
Quality Checks
For optimal results, you need to perform constant water quality checks. Imbalances in the nutrient or pH level and temperature variations can affect the growth of the plants. At the same time, you need to ensure the fish stay healthy.

Further checks involve the efficiency of filters, drains, and pumps. You don’t have to do these checks every day, but you can’t skip them either.
Types of Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics systems circulate water in different ways. They may or may not use a timer, a light source, or a drain.
Here are the key systems you should know about. Remember that you can always adapt them to your needs by adding to them small variations.
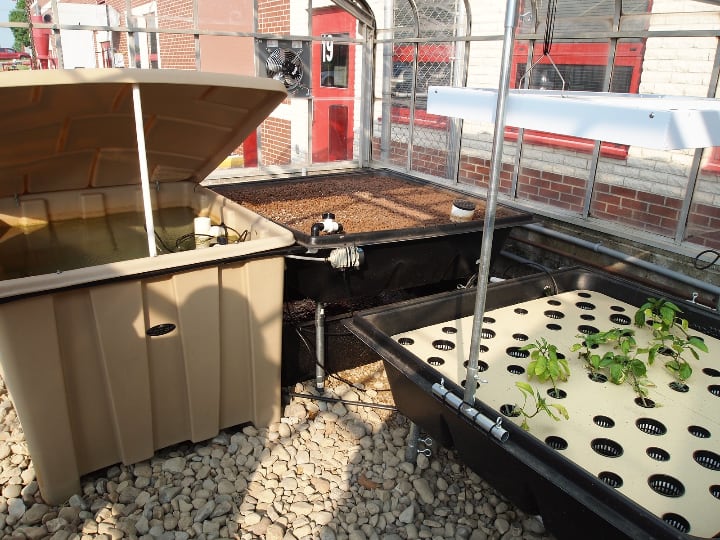
Media-Filled Beds
The simplest aquaponics systems use containers filled with expanded clay pellets or porous rocks that facilitate plant growth. These systems are easy to set up. They use hydroponics to pump the water over the media-filled beds.
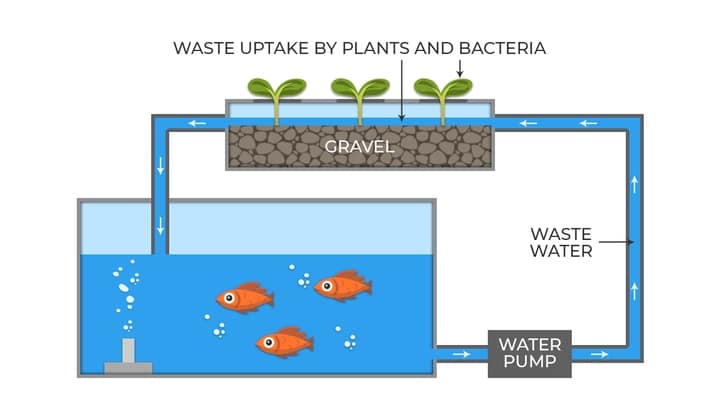
Alternatively, gravity can drain the water from the grow bed. The porous rocks hold water for longer than plain rocks, provide efficient aeration, and filter out biological organisms and parasites.
Aquaponics systems using media-filled beds come in two configurations. Take a quick look at each below.
Continuous Flow Media Filled Beds
Continuous flow systems circulate water from the aquaculture tank through the media bed and then back into the tank. They require a pump and need to be properly set up to remain efficient.

Pros
- Effective aeration and nutrient dynamics
- Relatively easy to set up compared to other systems
- Perfect for beginners
Cons
- An interruption in the flow can disrupt the entire system
- Grow conditions can be affected by the quality of the porous rocks
Ebb and Flow Media-Filled Beds
Ebb and flow aquaponics rely on a timer to pump water into the media-filled beds at regular intervals.
They operate to a depth of 10” or more before draining the water away using a siphon. These systems use resources effectively and provide good plant aeration.

Ebb and flow aquaponics can be adapted to large scale use. But effective operation depends largely on the timer.
Any malfunction with the timer can result in disruption. Also, this system can become clogged with fish waste and so requires regular cleaning.
Pros
- Easy to scale
- Energy-efficient
- Simple to set up
Cons
- Requires more frequent cleaning than other systems
- Timer-dependent
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Aquaponics
The NFT system in aquaponics runs nutrient-rich water from the aquaculture tank through a series of growing pipes.
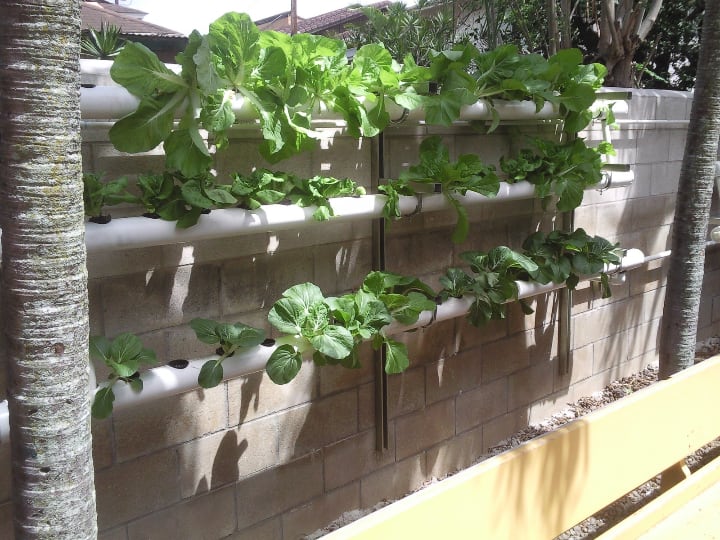

The plants sit in special holes in the pipes, often within net pots. Air gaps above the water level ensure high humidity oxygenation.
The water circulates slowly along the pipe as a thin film, hence the name. At the end of its circuit, the water returns to the fish tank. Depending on the system, the pipes can be either PVC pipes or enclosed gutters.
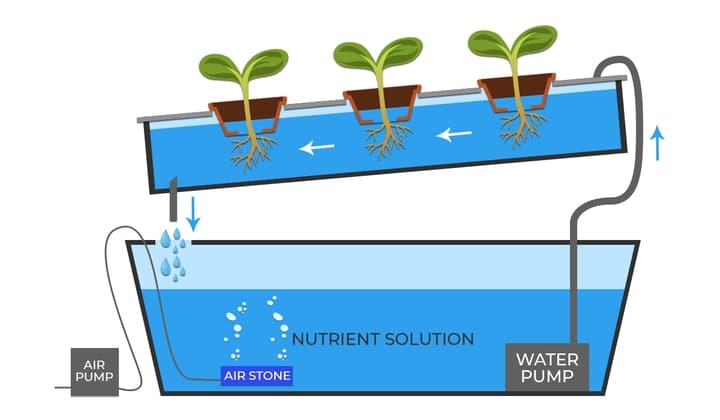
Good to know: NFT aquaponics requires a biological filter to convert fish waste into plant nutrients and promote the development of beneficial bacteria. At the same time, it calls for the adequate filtration of waste solids.
NFT aquaponics systems are not equally effective for all types of plants. They’re not ideal for plants with extensive roots like potatoes or sweet potatoes.
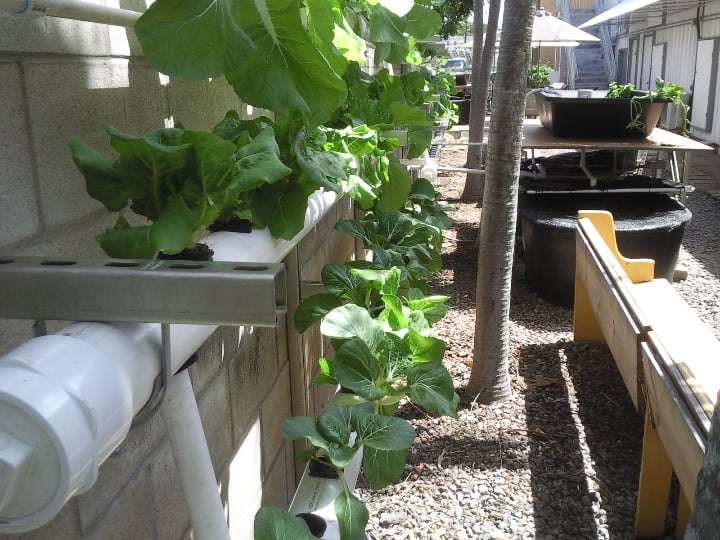

However, they are perfect for growing lettuce or watercress fast and without any hassle.
Pros
- Uses water efficiently
- Great for leafy greens
- Can be installed vertically to save up space
Cons
- Not ideal for plants with extensive root systems
- Requires multiple filters for effective operation
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Aquaponics
In the deep water culture system, the plants float on the surface of the aquaculture tank with their roots hanging in the water.
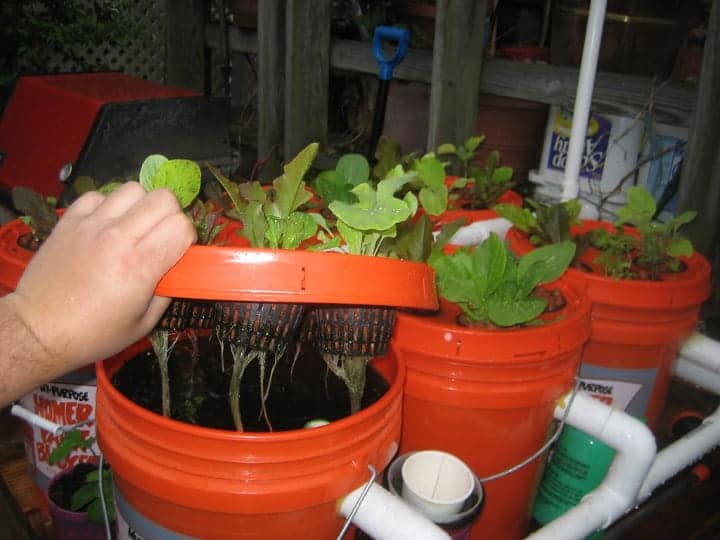

The plants sit on Styrofoam containers with holes in the bottom or directly on rafts with the filtration system attached.
One limitation of DWC aquaponics is that it cannot sustain the growth of plant-eating fish species as these may attack the roots of the plants.
DWC aquaponics doesn’t require complex equipment. But it does call for an air pump to oxygenate the tank as well as a solid waste filter.
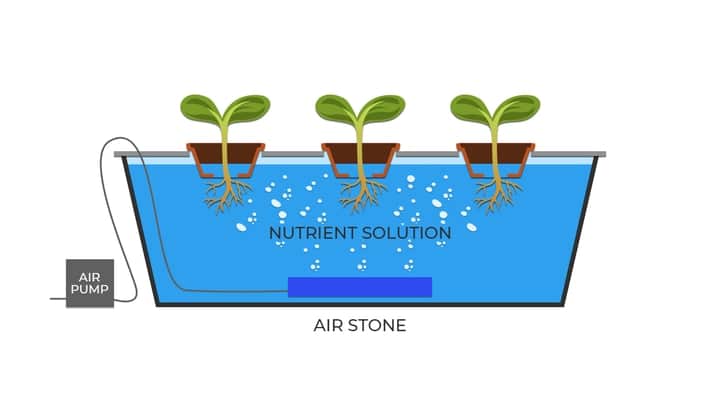
It’s frequently applied in commercial settings because it can produce high yields and allows for easy harvesting.
The big advantage of the deep water culture system is that the water doesn’t circulate through other system parts.
By remaining in the aquaculture tank at all times, it maintains a balanced temperature and pH and creates a stable environment for the fish and the plants to thrive.
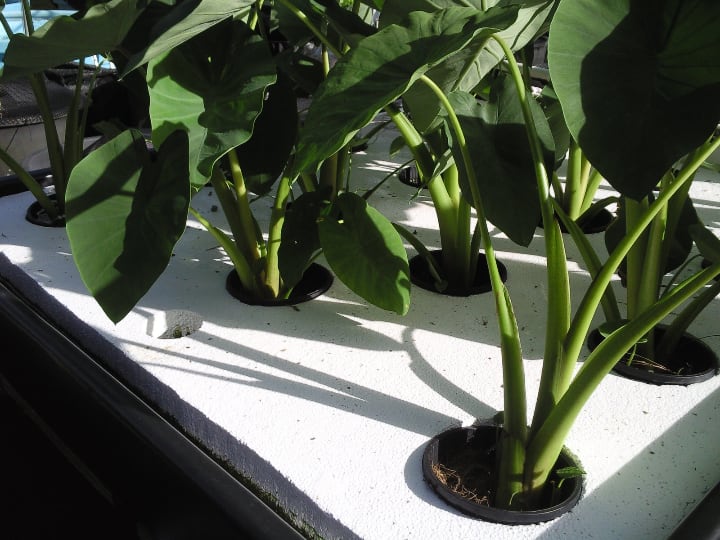

Pros
- Stable system conditions drive fast growth
- Easy to scale to increase yield
- Effective for large scale farming
Cons
- Limits the varieties of fish you can use
- Can be harder to deploy than other systems
How to Choose the Right Aquaponic System for You
As you can see, aquaponics systems come in many shapes and sizes. Knowing what you’re looking for can save you time and money. Not least, it can help you get a better return for every dollar you spend.
Here are the main considerations you need to pay attention to.
Size of the System
Small systems tend to be easier to maintain and more energy efficient. If a component fails over time, it will usually be cheaper to repair.
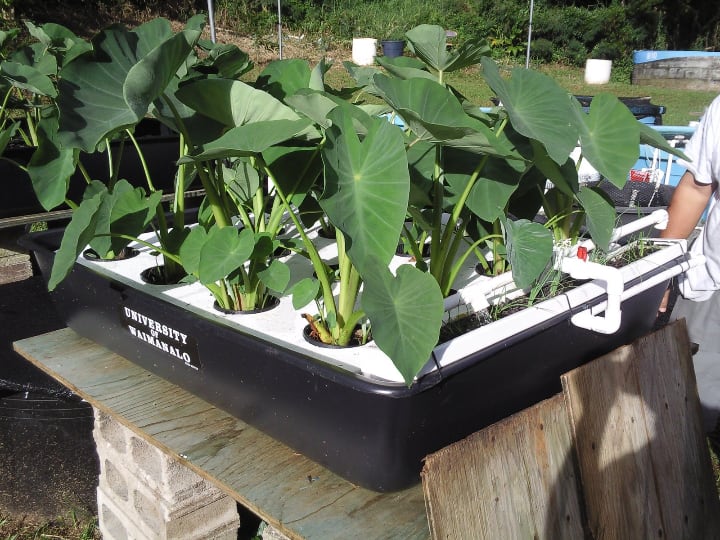

But not all small systems are scalable. For example, a deep water culture aquaponics system is more scalable than say a nutrient film aquaponic system.
Aquaponic System Maintenance
Most aquaponics systems offer some level of self-regulation. But don’t forget that you still have to feed the fish and keep the system clean.
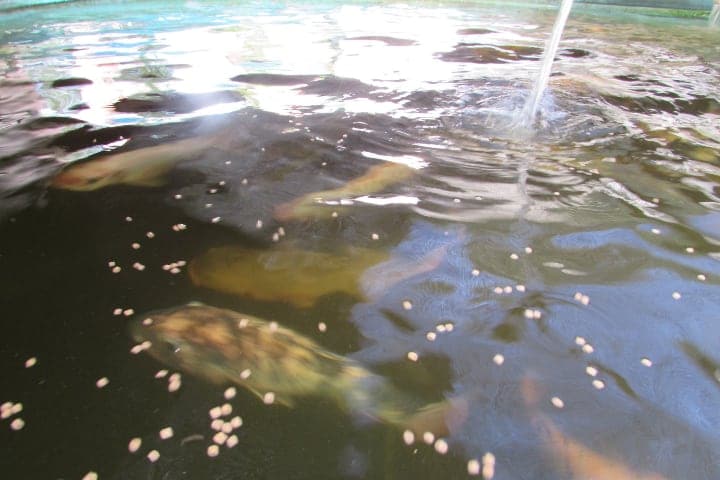

Depending on the water circulation system you use, you may have to perform more—or less—maintenance.
Energy Efficiency
Is energy efficiency important for you? Consider how much water and electricity the aquaponic system uses. Extras like LED lights, timers, or pumps will increase electricity usage.
Plants
Good news—plants for aquaponics range from herbs and lettuce to veggies and ornamentals. But not all setups work for all types of plants.
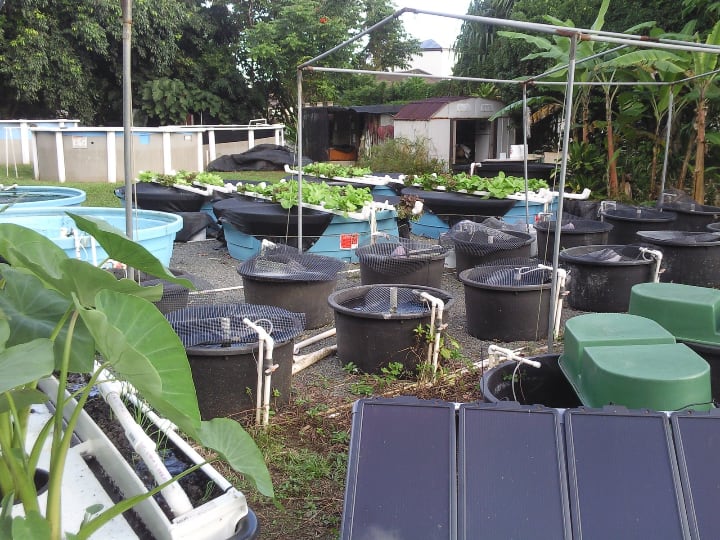

Consider the size of the planting area and grow support. These can limit what you can grow. If you plan on growing ornamentals or more nutrient-demanding plants, go for a larger setup.
Fish
Most fish in home aquaponic setups are small, but they need space to grow. The size of the fish tank will influence the types of fish you can grow. Also, it will determine how many fish you can keep.
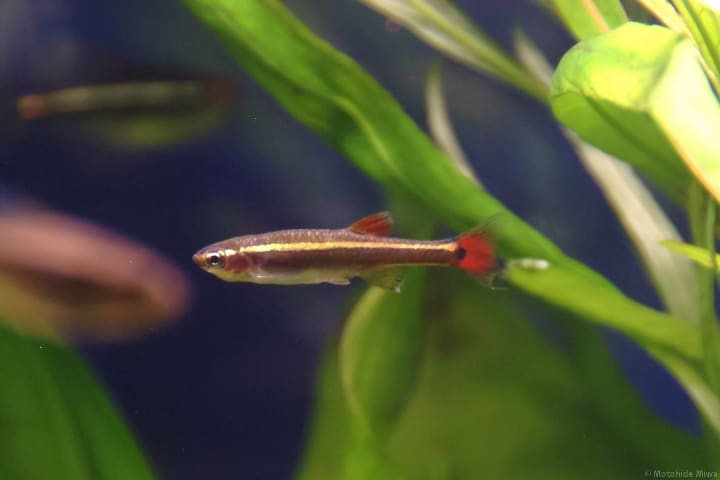

Most setups facilitate the growth of very small fish like the betta, cloud minnow, or goldfish. Want to grow larger fish? Consider investing in a DIY aquaponics kit for large fish tanks or garden ponds.
What Are the Best Plants for Aquaponics?
Aquaponics works best with plants that do not demand many nutrients. You can use it to grow vegetables like tomatoes or cauliflowers as well as strawberries and other fruits.
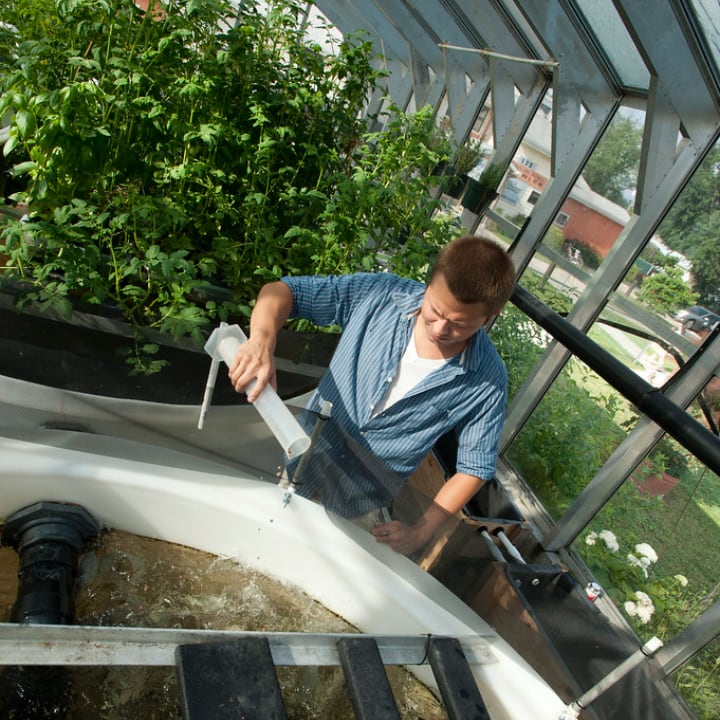

But many users find it easier to grow lettuce, watercress, kale, and other leafy vegetables, as well as certain herbs.
Here’s an essential list of the best plants for aquaponics.
- Lettuce
- Watercress
- Kale
- Basil
- Microgreens
- Ginger
- Peppers
- Tomatoes
- Cucumbers
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Strawberries
- Sweet corn
- Asparagus
- Onions
Ornamental plants for aquaponics include violas, roses, orchids, and other species that like growing in moist environments or directly in water.
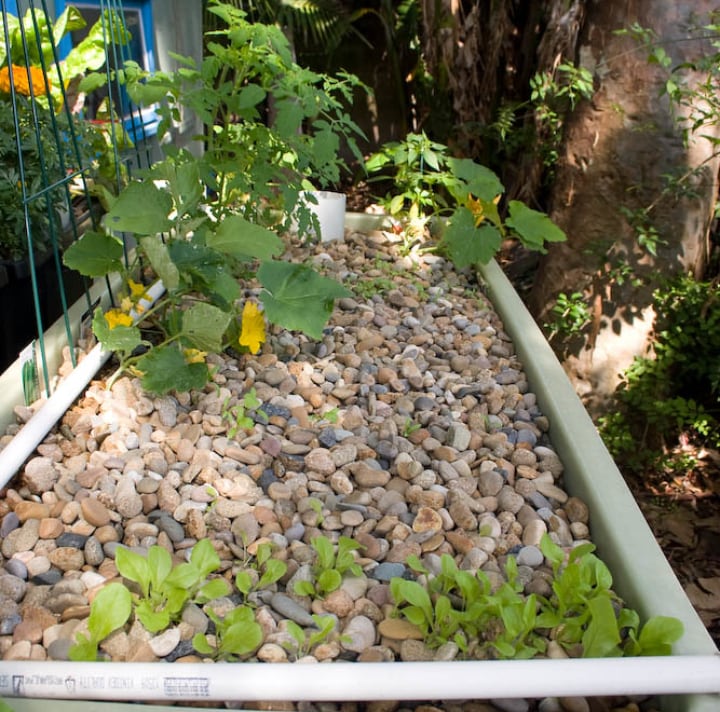

Plants that don’t grow so well in an aquaponic system include mint, broccoli, beans, peas, squash, blueberries, citrus fruits, and chrysanthemum.
What Fish Are Good for Aquaponics?
Some fish species are better suited for aquaponics systems than others. Key factors at play include growth rate, size, eating habits, and longevity.
Other things to consider when choosing the right fish for your aquaponic adventure are water temperature and if your fish are omnivores or carnivores.
Find below a quick overview of different types of fish that work well in aquaponic systems and the environment they thrive in.

If you’re just getting started, here are the fish species you should focus on as an aquaponics beginner.
Goldfish
Goldfish are fairly easy to grow and feed. They are beautiful ornamental fish that can thrive even within small systems.
Koi
If you don’t plan on eating the fish, you want some koi in your fish tank. Koi fish are colorful, adaptable, and tend to live long.
Tilapia
Tilapia are easy to breed and help keep the system clean by eating algae. But they do require warm water.
Trout
Suitable for outdoor aquaponics, trout grow fast and have very good food to growth ratio.
Catfish
Catfish have a high nutritional value and can adapt to most aquaponics systems. But to thrive, they require a varied diet that includes plants and insects.
Building Your Own Aquaponics DIY System
Can you make your own aquaponics DIY system at home? You bet! You’ll need a fish tank, a dependable water pump with a timer, a plant bed, and a few other small items you can readily get.
Follow our guide to upgrade a fish tank into an aquaponic system.
Step 1 – Get the Plant Bed Ready
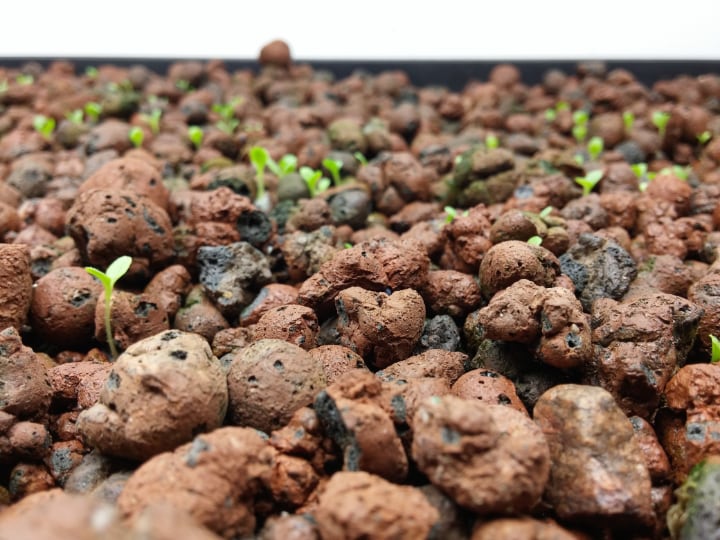

Install your plant bed over the fish tank. The plant bed can be a long window pot or a similar plastic container. Choose something durable but not very heavy.
Step 2 – Install the Pump
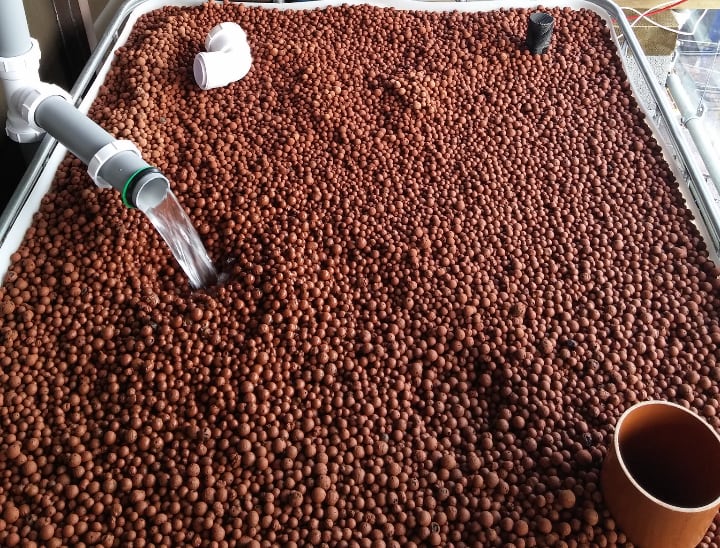

Next, install the pump in a corner of the fish tank where it won’t bother the fish. Place the pipe so that it brings water up to the plant bed.
Step 3 – Add a Drain
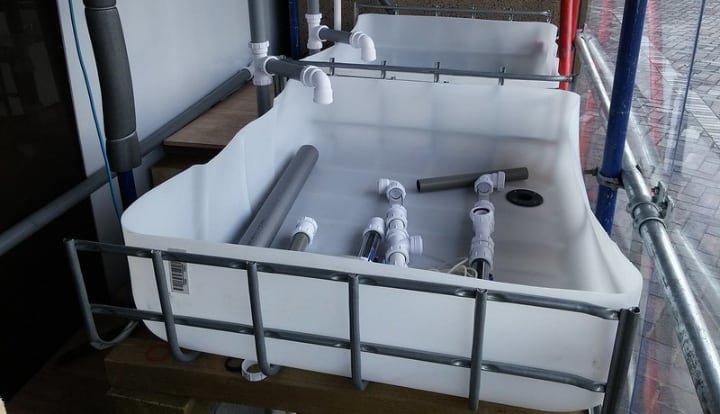

Before filling the plant bed with the grow medium of choice, make a hole at the opposite end from where the pipe is.
Put a PVC pipe through it with a media guard on top. This will act as a drain than returns the water into the fish tank.
Step 4 – Create a DIY Waste Filter
You need to prevent solid fish waste from making its way into the grow medium. To do this, wrap up the end of the pipe that empties into the grow bed into some aquarium filter floss.
Step 5 – Install a Timer
Add a timer to the pump and set it to 15-20 minutes. The timer will dictate how often the water will flow the grow bed.
Step 6 – Add a Light Source

An optional component you may want to install is a light source for the plants. This can be a LED lamp.
The steps are easy so you shouldn’t have any trouble following them.
Check out also this inexpensive setup that offers a great introduction to aquaponics and doesn’t require a big initial investment. Here’s a video that shows it in action.
If you’re into fish growing and hydroponics, you may already have at least some of the components you need to get it running.
Aquaponics Kits
The easiest way to get started growing plants and fish is through an aquaponic system for the home.
There are plenty of aquaponics kits out there for both beginners and advanced users. They are easy to set up and run.
Here are some of the best ones you can buy.
Ecolife Aquaponics Indoor Garden System with LED Light
This indoor garden system from Ecolife is easy to set up. The best part is that you don’t have to change the water.
Once it’s up and running, you only have to tweak the programmable LED lights—you have four grow settings to choose from. Extra features include a built-in timer and remote control.
Back to the Roots Water Garden
This mini-ecosystem for the home relies on the basic principles of aquaponics. It creates a simple hydroponic circuit through which fish waste fertilizes the microgreens on top.
With this kit, you can grow salad and herbs in around 10 days. Not bad, right?
Note: You’ll have to buy the fish separately.
Penn Plax Aquaponic Betta 1.4 Gallon Fish Tank
This aquaponics planter and fish habitat combo is easy to set up and use. Even if you’ve had a more sophisticated aquaponics system before, you’ll appreciate its simplicity.
The fish waste gathers in the fishbowl at the bottom of the tank and goes on to fertilize the plant at the top of the tank.
In turn, the plant helps keep the fish’s habitat clean by absorbing the waste through its roots.
AquaSprouts Garden
A self-sustaining aquaponics kit, the AquaSprouts Garden installs over just about any 10-gallon fish tank (not included). The kit comes with a pump and timer, adjustable light bar, clay grow media, and setup guide.
The system recirculates clean water after filtering it through the grow bed. You’ll like the quiet flow of the water and relatively spacious grow bed. With it, you can grow veggies, greens, and simple decorative plants.
Aquaponics Floating Pond Planter Basket
This planter basket is not a complete aquaponics kit in itself. But its versatility makes it worth mentioning. It features DIY floating plant baskets made from buoyant PVC that you can use for medium and large-sized ponds.
The baskets protect the plants from the fish while providing your finned friends with shade.
AquaParts S2 Aquaponics Plumbing System
This plumbing system from AquaParts features 27 parts that you can use to build a DIY aquaponics system. To get it up and running, you’ll need a fish tank and two grow beds which you’ll have to buy separately—or improvise from things you have at home.
The kit includes siphons, media guards, tubing, and extensive instructions. Even if you’re new to hydroponics, you shouldn’t have too much trouble setting this one up.
Aquaponics FAQS
We get a lot of questions from our readers on aquaponic systems, kits, and how to use them.
We put together the most frequently asked questions on aquaponics here and answered them for you. Explore now the answers!
What can be grown with Aquaponics?

With aquaponics, you can grow many types of plants including basil, ginger, kale, lettuce, watercress, cabbage, cucumbers, peppers, cauliflower, tomatoes, strawberries, carrots, onions, and more. You can also grow certain ornamental flowers including roses and tulips.
What does Aquaponic mean?

Aquaponics combines cultivating plants in water (hydroponics) with raising fish, prawns, snails, and other aquatic creatures in tanks (aquaculture). Aquaponics relies on different systems to create a symbiotic environment.
Is Aquaponics better than Hydroponics?

Aquaponics is a development of hydroponics that comes with all its benefits—faster plant growth, higher yield, reduced use of resources—and the added benefit of using aquaculture to create a fully sustainable ecosystem that requires less maintenance. But aquaponics may have higher running costs.
Can Orchids grow in Aquaponics?

You can use aquaponics to grow orchids provided that you feed them the right nutrients. The thing to note is that orchids prefer moist rather than wet soil. So, you may have to adapt your aquaponic system to get the best results. Explore now the best plants for aquaponics.
The Best Time to Get Into Aquaponics Is Now
Aquaponics is a great way to recreate the cycles of nature to grow plants and fish sustainably. You don’t have to be a hydroponics expert to get started.
Nor do you need to have previous experience with aquaculture. You can adapt aquaponics systems to indoor or outdoor use and scale them according to your needs.

At the end of the day, aquaponics is not just an effective way to farm but an enjoyable process. Watching the fish and the plants thrive together in the sustainable environment you’ve created can be deeply rewarding. And quite zen, too!
Do you still have any questions about aquaponics? Write to us in the comments box and let us know. We’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
And if you enjoyed this post, don’t forget to share it. Let’s spread the word about aquaponics together!



Leave a Reply